Medicare Prescription Drug Coverage
Medicare drug coverage helps pay for prescription drugs you need. To get Medicare drug coverage, you must join a Medicare-approved plan that offers drug coverage .
Learn more about how to get Medicare drug coverage.
Each plan can vary in cost and specific drugs covered, but must give at least a standard level of coverage set by Medicare. Medicare drug coverage includes generic and brand-name drugs. Plans can vary the list of prescription drugs they cover and how they place drugs into different “tiers” on their formularies.
More States Easing Into Expansion
New Hampshire, Michigan, Indiana, Pennsylvania, Alaska, Montana, and Louisiana all expanded their Medicaid programs between 2014 and 2016. Expansion took effect in Virginia and Maine in 2019, in Utah, Idaho, and Nebraska in 2020, and in Oklahoma in 2021. It might also take effect in Missouri in 2021, depending on the outcome of the lawsuit over Missouris voter-approved ballot measure that calls for Medicaid expansion.
The 2018 election was pivotal for Medicaid, with three states passing ballot initiatives to expand Medicaid, and Kansas, Wisconsin, and Maine electing governors who are supportive of Medicaid expansion .
The first six states to implement Medicaid programs did so in 1966, although several states waited a full four years to do so. And Alaska and Arizona didnt enact Medicaid until 1972 and 1982, respectively. Eventually, Medicaid was available in every state, but it certainly didnt happen everywhere in the first year.
What Do Medicare And Medicaid Cover
Medicare Part A is hospital insurance and Part B is medical insurance. Medicare Part D is prescription drug coverage, and Part C is an all-in-one coverage option that combines Parts A, B and D, as well as other benefits that may include items like dental, vision, fitness and hearing. Medicare Part A and Part B coverage is standard, but Part C and Part D will vary based in terms of coverage provided depending on the plan, the insurance provider and your location.
Medicaid programs include federally mandated benefits and optional benefits. Each state decides what optional benefits to include.
Read Also: When Does Medicare Part D Start
Medicaid Eligibility And Costs
The federal/state partnership results in different Medicaid programs for each state. Through the Affordable Care Act , which was signed into law in 2010, President Barack Obama attempted to expand healthcare coverage to more Americans. As a result, all legal residents and citizens of the United States with incomes of up to 138% of the poverty line qualify for coverage in Medicaid participating states.
While the ACA has worked to expand both federal funding and eligibility for Medicaid, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that states are not required to participate in the expansion in order to continue receiving already established levels of Medicaid funding. Many states have chosen not to expand funding levels and eligibility requirements.
Those covered by Medicaid pay nothing for covered services. Unlike Medicare, which is available to nearly every American of 65 years and over, Medicaid has strict eligibility requirements that vary by state.
However, because the program is designed to help the poor, many states require Medicaid recipients to have no more than a few thousand dollars in liquid assets in order to participate. There are also income restrictions. For a state-by-state breakdown of eligibility requirements, visit Medicaid.gov and BenefitsCheckUp.org.
How Many Americans Are Enrolled In Medicaid
As of September 2020, there were 77.3 million people enrolled in Medicaid and Childrens Health Insurance Program coverage in the United States. Most are enrolled in Medicaid, although 6.7 million are enrolled in separate CHIP coverage. Including separate CHIP and Medicaid, children account for about half of the 77 million enrollees .
Recommended Reading: What Is Better Original Medicare Or Medicare Advantage
What Are Dual Special Needs Plans
Dual health plans are also known as dual special needs plans. Theyre offered by private insurance companies, so you can find a dual health plan that best meets your health insurance needs. Being on a dual health plan does not change your Medicaid eligibility or benefits.
See UnitedHealthcare plans in your area.
Please note that the specific benefits dual health plans include can change depending on where you live. Search by your ZIP code to find the right plan to meet your health care needs.
Resource Center
Were here to help.
Contact us at:
Were here to help.
Contact us at:8 a.m. to 8 p.m. local time, 7 days a week.
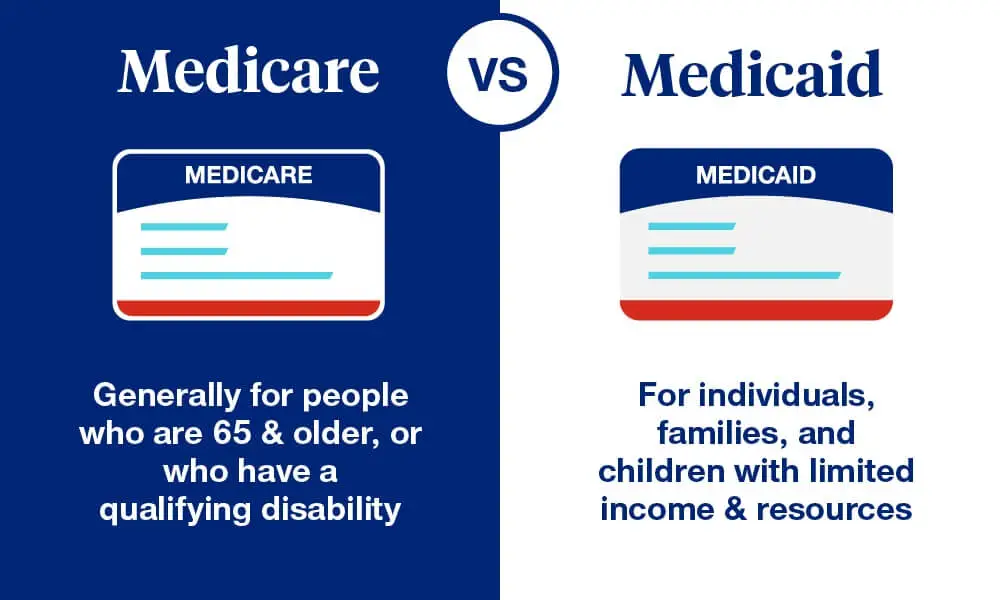
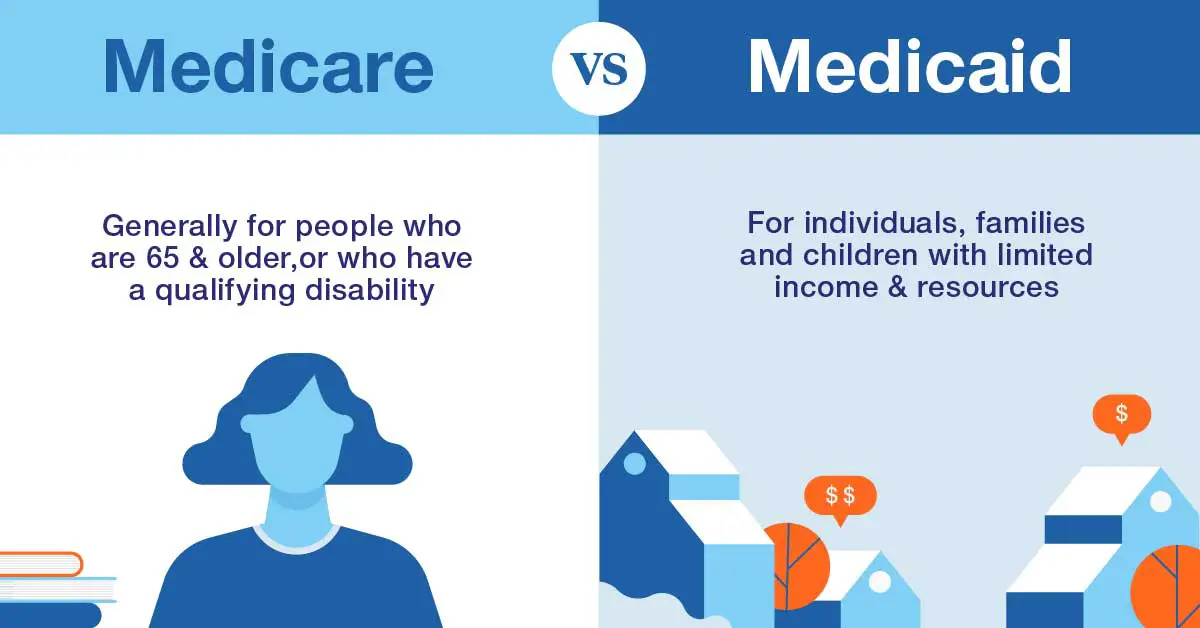
Medicare Vs Medicaid: Eligibility
Medicare: Youre eligible once you turn 65, as long as youre a U.S. citizen or legal permanent resident. Medicare also covers younger people with disabilities and certain diseases, including end stage renal disease and Lou Gehrigs disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis . People with higher incomes pay larger premiums for certain parts of Medicare, but eligibility isnt limited by income.
Medicaid: Medicaid coverage is based on income. Medicaid is available in every state to those with incomes below the poverty line. Under the Affordable Care Act, most states have expanded Medicare eligibility to people with incomes up to 133% of the federal poverty line.
Don’t Miss: When Are You Eligible For Medicare Part A
Who Is Eligible For Medicaid
Every state in the United States has its own set of eligibility requirements for Medicaid. Generally, though, in order to qualify you have to belong to one of the following groups:
- Families ,
- Pregnant women
- Adults with income up to 138% of the poverty level
In addition, each state considers three factors:
The Medicaid program is means-tested. In order for you to qualify for the healthcare benefits under Medicaid, you have to actually provide evidence that youre poor or that youre suffering from the disabilities that you claim. Additionally, in the states that havent expanded Medicaid under Obamacare, being poor alone doesnt necessarily mean youll qualify for coverage.
HealthCare.com offers a quick tool below to help you figure out if you might qualify for Medicaid. Keep in mind that its just a predictor tool and it makes a prediction based on your income alone
What Counts as Poor? Are You Poor Enough for Medicaid?
What counts as poor will vary from state to state. Generally, some percentage of the federal poverty level is used as a guideline for states.
Whether youre considered poor enough for Medicaid all depends on where your income compares to the FPL and what your states eligibility requirements say. You potentially fall into one of three camps:
How Can I Apply
Now that you know about the differences between the two programs, who is eligible, and what is covered, you are probably wondering how you can apply for them. Lets start with Medicare. Enrollment in Original Medicare is automatic in many cases. Upon reaching the age of 65, you will be automatically enrolled in Medicare if you are already receiving Social Security retirement benefits. Also, you will be automatically enrolled after 24 months of receiving SSDI payments. If you do not receive retirement benefits, then you can apply for Part A coverage and start receiving coverage upon paying the premium amounts. You can apply for Medicare through the Medicare website or over the phone.
If you choose to delay enrollment, then you can enroll during the yearly Medicare open enrollment period. Waiting too long may require you to pay a late enrollment penalty to obtain coverage. In addition, if you choose to apply for Part B, C, or D coverage, then you should contact your insurance company or agent to discuss those options. Since those plans are administered by private companies, they each have their own rules about enrollment and pricing.
Don’t Miss: Does Medicare Pay Anything On Dental
Medicare Vs Medicaid Compare Benefits
In the context of long term care for the elderly, Medicares benefits are very limited. Medicare does not pay for personal care . Medicare will pay for a very limited number of days of skilled nursing . Medicare will also pay for some home health care, provided it is medical in nature. Starting in 2019, some Medicare Advantage plans started offering long term care benefits. These services and supports are plan specific. But they may include:
- Adult day care
Some Items Not Covered
Medicare covers eye examinations, but not eyeglasses. medicare will cover optical surgery, such as cataracts. Many durable goods, such as walkers, braces, etc. are available through medicare.
Medicare does not cover routine dental needs. Some procedures may be covered under special circumstances. If a dental issue requires a hospital stay, medicare will pay for the hospital stay but not the dental procedures.
Medicare does not normally cover the cost of staying in a nursing home. However, medicare will cover hospital-type procedures, laboratory tests, physical therapy, and other health services.
Complete information about medicare services and requirements may be found in a brochure published by the social security administration, entitled Medicare.
You May Like: Does Medicare Cover Any Weight Loss Programs
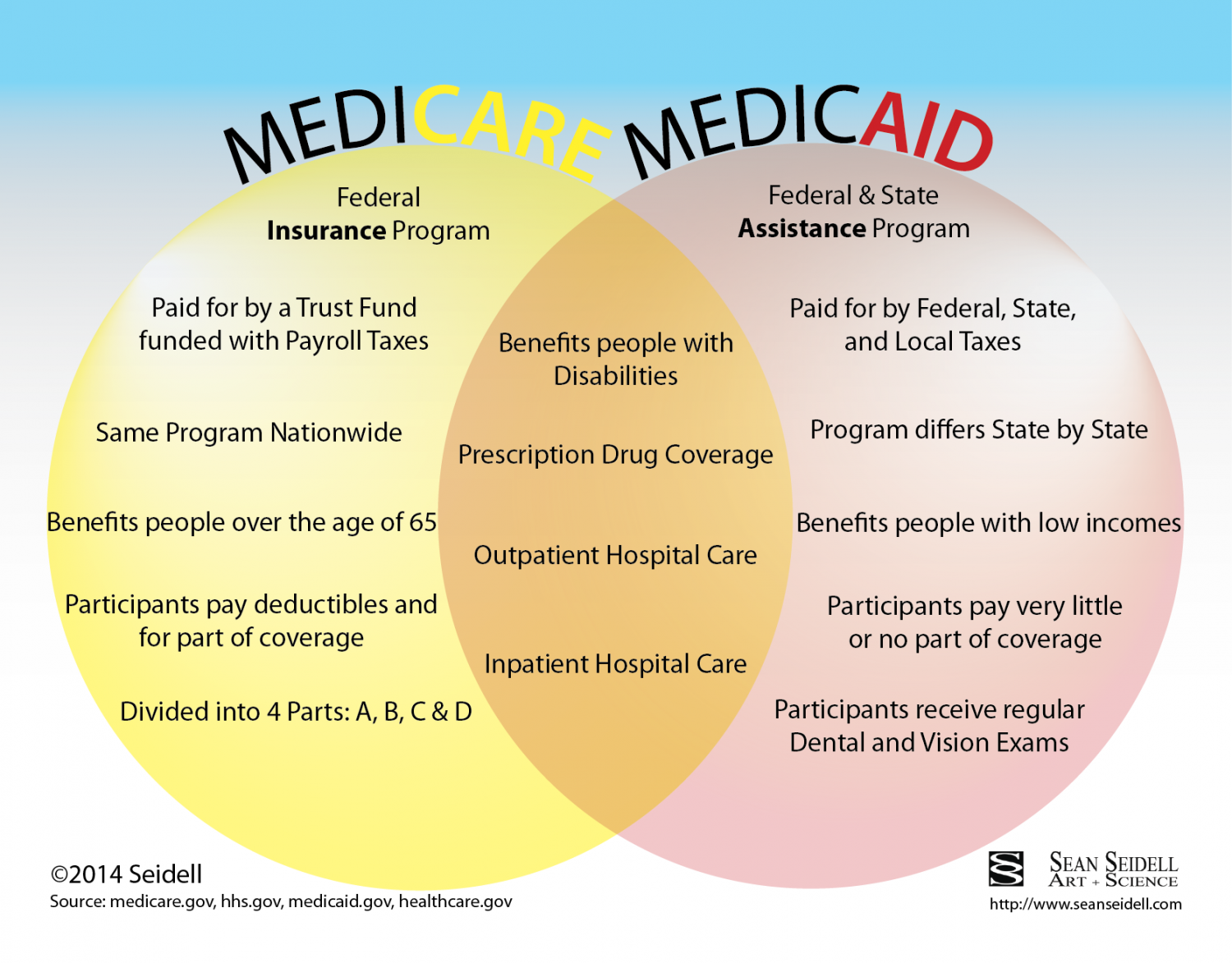
The Key Differences Between Medicaid And Medicare
Medicare and Medicaid are both government sponsored programs that assist with the cost of healthcare. Because the two programs have similar names, people often confuse how they work and the services they provide. While both programs are funded by taxes and were created by the federal government in 1965, the programs and the coverage they provide are very different.
Medicaid is a joint program between federal and state governments that provides medical and long-term care to low income individuals and families. The federal government provides up to 50% of the funding for each states Medicaid program with more affluent states receiving less from the federal government than less affluent states. Because of the partnership between the federal government and each state, there are essentially 50 different Medicaid programs.
Individuals who qualify for Supplemental Security Income through the Social Security Administration are automatically eligible for the insurance portion of Medicaid. Individuals can apply for Medicaid any time throughout the year even if they do not receive SSI.
It is important to note the differences between these programs, and it may be necessary to meet with an attorney to determine whether an individual is accessing the proper healthcare benefits and to insure techniques are properly utilized to allow an individual to become financially eligible for Medicaid.
Pittsburgh, PA1600 Law & Finance Building429 4th AvenuePittsburgh, PA 15219P: 412.313.5510
When Did The Medicaid Program Start
Medicaid became federal law in 1965, as part of Title XIX of the Social Security Act. Coverage became available in 1966, with about 4 million people enrolled in the program that year. But since its a joint program between the federal and state governments, states adopted the program at different times. Arizona was the last state to create a Medicaid program, doing so in 1982. Medicaid has been available nationwide since 1982.
Don’t Miss: How Much Is Medicare Part B Now
Whats The Difference Between Medicare And Medicaid
The difference between Medicaid and Medicare is that Medicaid is managed by states and is based on income.
On the other hand, Medicare is managed by the federal government and is mainly based on age.
However, there are special circumstances, like certain disabilities, that may allow younger people to get Medicare.
The chart below, summarized from United HealthCare provides in a clearer format the difference between Medicare and Medicaid.
What Are Dual Health Plans
Dual health plans are designed just for people who have both Medicaid and Medicare. Theyre a special type of Medicare Part C plan. Dual health plans combine hospital, medical and prescription drug coverage. Youll keep all your Medicaid benefits. Plus, you could get more benefits than with Original Medicare. And you could get it all with as low as a $0 plan premium.
View the “Do I Lose My Medicaid Benefits?” article.
Recommended Reading: Does Medicare Pay For Foot Care
Effective Date Of Coverage
Once an individual is determined eligible for Medicaid, coverage is effective either on the date of application or the first day of the month of application. Benefits also may be covered retroactively for up to three months prior to the month of application, if the individual would have been eligible during that period had he or she applied. Coverage generally stops at the end of the month in which a person no longer meets the requirements for eligibility.
Medicaid Expansion With A Ballot Initiative
In Maine, Utah, Idaho, Nebraska, and Oklahoma, Medicaid expansion came about as a result of ballot initiatives passed by voters. Voters in Missouri passed a similar ballot measure in 2020, but GOP lawmakers in the state have delayed implementation by refusing to fund the states portion of the cost. A lawsuit has been filed and the trial is scheduled for June 2021.
So far, Medicaid expansion ballot initiatives have passed in 100% of the states that have had them on the ballot .
In early 2021, Medicaid expansion advocates in Florida, Mississippi, and South Dakota were working towards possible expansion ballot measures for the 2022 election .
Recommended Reading: Does Medicare Cover Hiv Medication
The Cost Of Not Expanding Medicaid Eligibility
Because the federal government funds nearly all of the cost of Medicaid expansion, the 14 states that havent yet taken action to expand Medicaid have been missing out on significant federal funding more than $305 billion between 2013 and 2022.
Just five states Florida, Texas, North Carolina, Georgia, and Tennessee would have received nearly 60% of that funding if they had expanded Medicaid to cover their poorest residents starting in 2013. The good news is that although the federal government is no longer funding the full cost to expand Medicaid, theyll always pay at least 90% of the cost, making the state Medicaid expansion a good deal for states regardless of when they implement it .
For residents of states that havent expanded Medicaid, their federal tax dollars are being used to pay for Medicaid expansion in other states, while none of the Medicaid expansion funds are coming back to their own states. From 2013 to 2022, $152 billion in federal taxes will be collected from residents in states not expanding Medicaid, and will be used to fund Medicaid expansion in other states.
Medicare And Medicaid Funding
Medicare is funded:
- In part by the Medicare payroll tax
- In part by Medicare recipients premiums
- In part by general federal taxes
The Medicare payroll taxes and premiums go into the Medicare Trust Fund. Bills for healthcare services to Medicare recipients are paid from that fund.
Medicaid is:
- Partially funded by the federal government
- Partially funded by each state
The federal government pays an average of about 60% of total Medicaid costs, but the percentage per state ranges from 50% to about 77%, depending on the average income of the state’s residents .
Under the ACA’s expansion of Medicaid, however, the federal government pays a much larger share.
For people who are newly eligible for Medicaid due to the ACA , the federal government paid 100% of the costs from 2014 through 2016.
States began to pay 5% of the cost in 2017, and that increased to 6% in 2018, and to 7% in 2019. From 2020 onward, states will pay 10% of the cost and the federal government will pay 90%.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Dental On Medicare
Work Requirements For States That Have Expanded Medicaid:
Work requirements that were in effect in early 2020 but have since been suspended:
- Michigan 80 hours per month . A federal judge overturned the states Medicaid work requirement in early March 2020, so residents are not currently required to comply with it.
- Utah beneficiaries are exempt from the community engagement requirement as long as theyre working at least 30 hours per week. And there are numerous other exemptions for various populations. But people who werent exempt had to comply with the states community engagement requirements. This involved creating an account on jobs.utah.gov, completing an online evaluation and workshops, and applying for at least 48 jobs within a three-month period.
Medicaid expansion states where new governors withdrew pending work requirements:
Expansion states where work requirements have been approved by CMS but are not yet in effect as of late 2020:
Medicaid expansion states with pending work requirement proposals:
Lawmakers in Louisiana considered several work requirement bills in 2018, but none were enacted. Lawmakers in Pennsylvania passed Medicaid work requirement legislation in 2017 and again in 2018, but Governor Tom Wolf vetoed both bills.
Lawmakers in Alaska considered Medicaid work requirement legislation in 2019, but the measure did not advance to a vote.
Public Support For Medicaid Expansion
Public support for Medicaid expansion is relatively strong, even in Conservative-leaning states: In Wyoming , 56 percent of the public are in favor of Medicaid expansion. But the Republican-led legislature in Wyoming has consistently rejected Medicaid expansion, despite Republican former Governor Matt Meads support for expansion.
Voters in Utah, Idaho, and Nebraska all conservative-leaning states approved Medicaid expansion ballot initiatives in the 2018 election. And the same thing happened in Missouri and Oklahoma in 2020.
In Texas home to more than a quarter of those in the coverage gap nationwide a board of 15 medical professionals appointed by then-Governor Rick Perry recommended in November 2014 that the state accept federal funding to expand Medicaid, noting that the uninsured rate in Texas was unacceptable. But no real progress towards Medicaid expansion has been made since then, and U.S. census data indicated that 18.4 percent of Texas residents were uninsured in 2019 the highest rate in the country
There are several other states where the legislature or the governor or both are generally opposed to the ACA, but where Medicaid expansion has been actively considered, either by the governor or legislature or in negotiations with the federal government. These include Kansas, North Carolina, and Tennessee.
Recommended Reading: Are Medicare Advantage Premiums Deducted From Social Security
