Medicare Part B Excess Charges: What Are They And How Can You Avoid Them
Discover what Medicare Part B excess charges are, the states where they are legal and how you can avoid them when paying for doctors visits and other medical services.
by Zia Sherrell | Published March 25, 2021 | Reviewed by John Krahnert
Medicare Part B excess charges arent all that common, but they can be distressing when they arise. These charges are often unexpected and can potentially cause financial hardship when you can least afford it.
Thankfully, Part B excess charges need not trouble you. Understanding what these charges are and how to avoid them can help you reduce your risk of a confusing Medicare bill. In this article, we outline how to avoid Part B excess charges, and we detail the Medicare Supplement plans that can pay for Medicare excess charges.
Doctors Are Allowed To Charge Up To 15% More Than What Medicare Allows Andstill Be Medicare Providers
Medicare has its own list of providers…similar to a PPO.These doctors agree to certain to certain requirements from Medicare .The most important of these rules deals with how much they can charge.For any given medical procedure, there’s an agreed upon reimbursement rate.For example, for a doctor visit with a dermatologist , Medicare may list a rate of $80 reimbursement back to the doctor in agiven area.The doctor must agree to a list of reimbursements based on different healthcare codes to be a Medicare doctor.If not, Medicare will not reimburse the doctor for those services to Medicaremembers.Pretty straight forward.There’s a catch !
How Medicare Excess Charges Work
Lets say you need an echocardiogram to check your heart function. A doctor who accepts assignment from Medicare may charge $100 for the procedure. They would receive $80 from Medicare and send you the bill for the Part B coinsurance amount of $20. If you have a Medicare Supplement plan, your Medigap insurance plan will cover all or part of the Part B coinsurance .
If instead, you decided to attend a clinic that doesnt accept Medicare assignment, the doctor could impose a Medicare Part B excess charge of 15% on top of the $100 charge for the echocardiogram. Instead of $100, the total for the service would be $115.
The doctor may require you to pay the total bill upfront instead of submitting it to Medicare, in this situation. Youd then file a claim with Medicare for reimbursement. Medicare would cover 80% of the $100 Medicare-approved amount as before. You would pay the remainder, meaning your out-of-pocket cost would be a total of $35 rather than $20.
This example shows how Medicare Part B excess charges work with a relatively small medical bill. However, doctors can also impose Part B excess charges on much larger bills costing thousands of dollars.
Also Check: When Is The Last Day To Change Medicare Plans
The Medicare Excess Wrap
Doctors can choose to charge more than 15% above what Medicare allows andstill be Medicare providers.
Core Part A and Part B do not cover this 15% – the member will be responsible
The financial impact from Excess will only grow with time due to Medicarepressure on costs.
The G Plan supplement is the only Supplement plan that covers this 15% Excess charge.
Finally, let us help you! There’s no cost for our services and we have helped1000’s of California Seniors find the best supplement plan values.
It’s fast, easy, and free to you since we’re licensed Medicare SupplementAgents.
Some States Do Not Allow Excess Charges

That means that if you live in one of these states, you will not have to pay these charges. Here is a list:
- Connecticut
- Rhode Island
- Vermont
If you reside in one of these states, you may want to consider a Medigap Plan N. Medigap N is less expensive than Plan G but doesnt cover excess charges. If you live in a state that doesnt allow excess charges, why pay for a benefit that you will most likely not use?
Recommended Reading: How To Renew Medicare Benefits
Accepting Medicare Patients Vs Accepting Medicare Assignment
There are providers who see Medicare patients but do not accept Medicare Assignment. If a doctor accepts Medicare, it doesnt necessarily mean he or she accepts Medicare assignment and might charge you up to 15% more than the Medicare approved amount.
If you do not have a Medicare Supplement and use only Original MedicarePart A and B, you are still subjected to excess charges. You pay the standard coinsurance of 20%, plus the excess charge up to 15%.
For example, you visit the doctor and the office visit is $100. Your doctor accepts Medicare patients, but does not accept Medicare Assignment. You are billed the usual 20% coinsurance on the $100 visit , plus the 15% excess charge that Medicare does not cover . Your final bill is $35.
How To Avoid Part B Excess Charges
The most obvious way to avoid Part B excess charges is by only visiting doctors who accept Medicare Assignment. The easiest thing you can do is simply ask them if they accept assignment upon scheduling an appointment. You can also use the Medicare.gov physician finder tool to help speed up the process of finding a doctor who participates in Medicare. Additionally, you can supplement your Medicare coverage with a Medigap plan that protects you from excess charges.
Don’t Miss: Is Pace A Medicare Advantage Plan
Using A Provider That Opts Out Of Medicare
Certain doctors and other health care providers who dont want to work with the Medicare program may opt out of Medicare. Medicare doesnt pay for any covered items or services you get from an opt-out doctor or other provider, except in the case of an emergency or urgent need. If you still want to see an opt-out provider, you and your provider can set up payment terms that you both agree to through a private contract.
A doctor or other provider who chooses to opt-out must do so for 2 years, which automatically renews every 2 years unless the provider requests not to renew their opt-out status.
Find providers that opted out of Medicare. You can search by their first and last name, National Provider Identifier , specialty, or ZIP code.
About Part B Excess Charges
Medicare has a pre-approved amount they will pay for eligible treatment and services.
If a person has Medicare Part B, and the amount a physician or healthcare provider charges is higher than the Medicare-approved amount, the difference is called an excess charge.
An individual is responsible for payment of excess charges and these costs do not usually count toward an annual deductible.
Private insurance companies offer Medigap plans, also known as Medicare supplement insurance. Medigap plans aim to fill some of the gaps left by original Medicares out-of-pocket expenses.
Some plans even offer additional benefits, including emergency care provided outside the United States, and excess charges.
To be eligible for a Medigap plan, a person must have original Medicare parts A and B.
A separate monthly premium is payable to the private insurance company selling the Medigap plan.
If a person has Medicare Advantage , Medigap insurance cannot legally be sold to them.
Other Medigap eligibility requirements may apply, depending on the state in which an individual resides.
Each Medigap policy offers different benefits and levels of coverage.
Monthly premiums may vary depending on:
- the private insurance provider
- the state in which a person lives
- when an individual becomes eligible for Medicare
With these considerations in mind, a person may have up to ten different Medigap policies to compare, including plans A, B, C, D, F, G, K, L, M, and N.
Read Also: Is Everyone Eligible For Medicare
What Is A Medicare Part B Excess Charge
An excess charge happens when you receive health care treatment from a provider who does not accept the Medicare-approved amount as full payment. In these cases, a provider can charge you up to 15% more than the Medicare-approved amount.
There are some ways you can avoid paying Part B excess charges, and you may be able to find a Medicare Supplement Insurance plan that can cover these charges.
Medigap Policies Are Standardized
Every Medigap policy must follow federal and state laws designed to protect you, and it must be clearly identified as “Medicare Supplement Insurance.” Insurance companies can sell you only a “standardized” policy identified in most states by letters.
All policies offer the same basic
but some offer additional benefits, so you can choose which one meets your needs. In Massachusetts, Minnesota, and Wisconsin, Medigap policies are standardized in a different way.
Each insurance company decides which Medigap policies it wants to sell, although state laws might affect which ones they offer. Insurance companies that sell Medigap policies:
- Don’t have to offer every Medigap plan
- Must offer Medigap Plan A if they offer any Medigap policy
- Must also offer Plan C or Plan F if they offer any plan
Read Also: How To Order Another Medicare Card
How Can You Avoid Medicare Part B Excess Charges
The easiest way to avoid facing Medicare Part B excess charges is to limit yourself to visiting providers and medical suppliers who accept Medicare assignment. As mentioned above, most providers and physicians accept Medicare assignment.
Be sure to ask your provider, device supplier or physician if they accept Medicare assignment before receiving any treatment or services.
There are also other ways you may be able to avoid paying Medicare Part B excess charges.
Some states do not allow Part B excess charges
There are eight states that have laws prohibiting Medicare Part B excess charges.
These states are:
| 80% | 80% |
Medigap Plans F And G
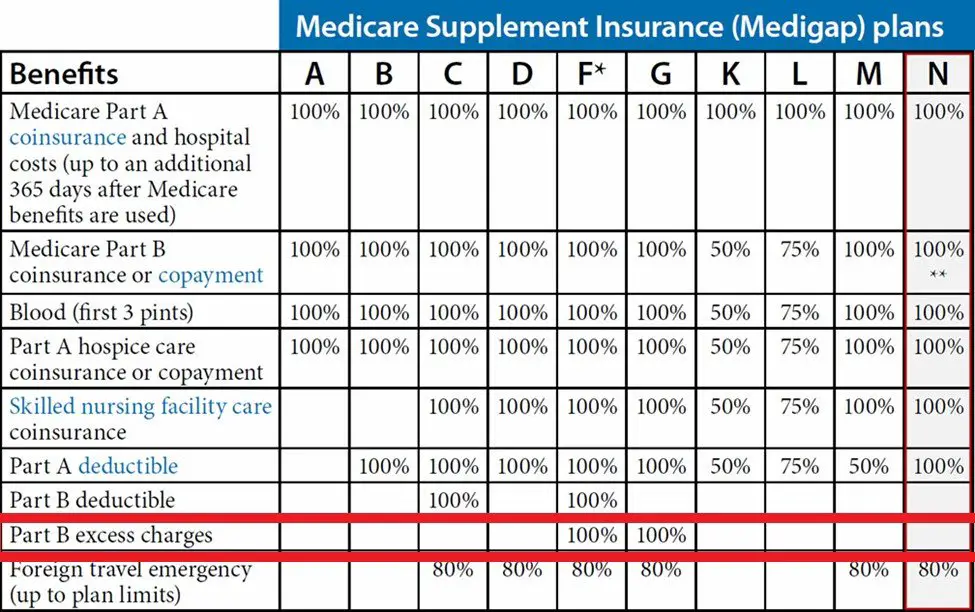
Medigap plans F and G may cover Part B excess charges. High-deductible versions of both of these plans are available in some states.
However, as of January 1, 2020, plan F is not available to those newly eligible for Medicare. Medigap policies that provided coverage for the Part B deductible are also no longer available for new enrollees as of January 1, 2020.
If a person needs help choosing a Medigap policy, they can contact their State Health Insurance Assistance Program .
For more information on state Medigap policies, an individual can contact the State Department of Insurance.
Also Check: Do Most Doctors Accept Medicare
Buying Medicare Supplement Plan F G Or N
You might want to try to predict your future health care needs when you are first enrolling in a Medicare Supplement insurance plan, as you may not be able to switch plans later when your needs change. In most cases, you wont have a right under federal law to switch Medicare Supplement insurance policies unless youre in your 6-month Medicare Supplement Open Enrollment period. During this Open Enrollment Period, you can buy a Medicare Supplement insurance plan from any insurance company thats licensed in your state.
This Open Enrollment Period begins on the first day of the month in which youre both enrolled in Medicare Part B and age 65 or older. If you apply for a Medicare Supplement insurance plan after your OEP ends, you may be subjected to medical underwriting. Medical underwriting uses information on your past or current health problems to charge you more for coverage or even deny you coverage. You will not be subject to medical underwriting during your Medicare Supplement Open Enrollment Period.
The product and service descriptions, if any, provided on these eHealth Insurance Web pages are not intended to constitute offers to sell or solicitations in connection with any product or service. All products are not available in all areas and are subject to applicable laws, rules, and regulations.
New To Medicare?
Becoming eligible for Medicare can be daunting. But dont worry, were here to help you understand Medicare in 15 minutes or less.
Statement About Healthplanonecom And Privacy
At HealthPlanOne.com, we understand that the process of selecting the right health care coverage for an individual or family member is a personal one. Our goal is protect your privacy while ensuring that you are offered useful and comprehensive information to help you make your decision.
At HealthPlanOne.com, we also understand that relationships are built on trust. So we want to make sure that we clearly disclose to you the kind of information our website may collect and what we do with that information.
Read Also: What Is Medicare Part G
What Is A Medicare Assignment
When a patient receives a service, their provider has the option to accept assignment. When a provider accepts a Medicare assignment, it essentially means that the provider agrees to the Medicare-approved service amount and they wont bill the patient above that rate. The Medicare-approved amount is how much Medicare agrees to reimburse the provider for the given medical service or equipment. At times, the Medicare-approved amount is lower than what a health care provider charges.
When providers choose not to accept assignment, they could charge up to 15% higher than the Medicare-approved amount, leading to excess charges.
Medicare Part B Excess Charges And How To Avoid Them
- What are Medicare Part B excess charges and how can they affect your doctor bill? Learn how to avoid these potentially costly surprise medical bills.
When a Medicare beneficiary visits a doctor or other health care provider or receives an item of durable medical equipment , the amount they will be billed depends partly on the type of contract the provider holds with Medicare. If the provider doesnt accept Medicare reimbursement as payment in full, a beneficiary may have to pay Medicare Part B excess charges, which can potentially be quite costly.
In most cases, beneficiaries will pay whats called the Medicare-approved amount. This is a pre-determined amount that states how much Medicare will reimburse a health care provider for a particular service or item. Many providers have agreed in their contract with Medicare to charge no more than this amount.
But certain providers have a stipulation in their contract that allows them to charge up to 15% more than the Medicare-approved amount. This extra charge is called an excess charge and is found only in Medicare Part B coverage.
If you are charged Medicare Part B excess charges, you are typically required to pay the amount for your treatment or services up front. You then need to submit a claim to Medicare to get reimbursement for the amount of your total costs that Medicare will pay. This reimbursement amount will be 80% of the Medicare-approved amount for your service.
Read Also: Does Medicare Cover Knee Injections
What States Prohibit Part B Excess Charges
There are eight states where providers are prohibited from charging Part B excess fees. If you live in one of these eight states, you won’t have to worry about excess charges unless you get services in a state that allows them.
Because many of us travel, we recommend that you include Part B excess charges in your plan even if you live in one of these states.
Those states that prohibit excess charges are Connecticut, Massachusetts, Minnesota, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and Vermont.
What Are Excess Charges
For an Original Medicare enrollee, the excess charge is the difference between a doctors fee for service and what Medicare Part B has approved as payment for that service.
The excess charge only applies if the doctor doesnt accept assignment with Medicare, but has not opted out of Medicare altogether. In other words, theyre a non-participating provider.
When a non-participating provider bills Medicare, their approved amount is only 95 percent of what Medicare would approve for a participating provider . That 95 percent is paid partially by Medicare, and partially by the patient in the form of coinsurance . But then the non-participating provider is allowed to charge up to 15 percent more, on top of the amount that Medicare approves for the service. This additional amount is called an excess charge. Its either paid by the patient or by the patients supplemental coverage .
Because Medicare pays non-participating providers less than participating providers, the excess charge amounts to less than 115 percent of the normal Medicare-approved amount, as explained here.
Some states prohibit non-participating providers from billing Medicare patients for excess charges, or limit the amount to something less than 15 percent.
You May Like: Can You Use Medicare In Any State
How Medicare Part B Excess Charges Can Add Up
If you see a non-participating provider, youre on the hook for the coinsurance and deductible, plus the excess charges, unless you have a Medicare Supplement policy that pays the difference.
So, for example, if Medicare has assigned $1,000 to a particular service , with a participating doctor Medicare would pay the physician $800, assuming youve hit your Part B deductible, and youd pay the $200 coinsurance.
But the tab can be far worse. In the case of a serious health care condition or medical crisis, bills for $10,000 or $50,000 or worse could easily carry excess charges in the thousands.
Plus, suppliers of medical devices and equipment can levy Medicare Part B excess chargesbut theyre not limited to the 15% cap. And Medicare does not place an annual ceiling on your out-of-pocket spending.
How Can You Avoid Excess Charges

Most doctors, providers and suppliers accept assignment, but you should always double check to make sure.
You can also use the Medicare.gov Physician Finder tool to find a doctor in your area who participates in Medicare.
Neither Original Medicare nor Medicare Advantage plans cover excess charges.
However, two types of Medigap supplement insurance policies do.
Medigap Plans That Cover Excess Charges
There are 10 different types of Medigap plans. Each is designated by a letter and must follow federal and state laws designed to protect the policyholder.
Basic benefits must be the same for each type of plan, no matter where the plan is purchased. Cost is typically the only difference between Medigap policies of the same letter because insurance companies can adjust rates depending on several factors.
Get a Free Medicare Advantage Guide
Also Check: What’s The Eligibility For Medicare
