The Introduction Of Medicare Part C In 1997
Medicare Part C was introduced through the Balanced Budget Act of 1997, with coverage beginning in 1999. Medicare Part C plans, today sometimes called Medicare Advantage plans, are offered by private insurance companies that contract with Medicare.
Medicare Advantage plans work with a network of providers. Their coverage model is more similar to employer coverage than original Medicare.
These plans must offer at least the same coverage as original Medicare, and they often include additional coverage for services that Medicare doesnt cover, such as dental, vision, and prescription drug costs.
The Solvency Of The Medicare Hi Trust Fund
This measure involves only Part A. The trust fund is considered insolvent when available revenue plus any existing balances will not cover 100 percent of annual projected costs. According to the latest estimate by the Medicare trustees , the trust fund is expected to become insolvent in 8 years , at which time available revenue will cover around 85 percent of annual projected costs for Part A services. Since Medicare began, this solvency projection has ranged from two to 28 years, with an average of 11.3 years. This and other projections in Medicare Trustees reports are based on what its actuaries call intermediate scenario but the reports also include worst-case and best-case projections that are quite different .
Costs And Funding Challenges
Over the long-term, Medicare faces significant financial challenges because of rising overall health care costs, increasing enrollment as the population ages, and a decreasing ratio of workers to enrollees. Total Medicare spending is projected to increase from $523 billion in 2010 to around $900 billion by 2020. From 2010 to 2030, Medicare enrollment is projected to increase dramatically, from 47 million to 79 million, and the ratio of workers to enrollees is expected to decrease from 3.7 to 2.4. However, the ratio of workers to retirees has declined steadily for decades, and social insurance systems have remained sustainable due to rising worker productivity. There is some evidence that productivity gains will continue to offset demographic trends in the near future.
The Congressional Budget Office wrote in 2008 that “future growth in spending per beneficiary for Medicare and Medicaidthe federal government’s major health care programswill be the most important determinant of long-term trends in federal spending. Changing those programs in ways that reduce the growth of costswhich will be difficult, in part because of the complexity of health policy choicesis ultimately the nation’s central long-term challenge in setting federal fiscal policy.”
Recommended Reading: Does Medicare Pay For Mens Diapers
A Brief Look At Medicare Milestones
The 60s
- On July 30, 1965 President Lyndon B. Johnson made Medicare law by signing H.R. 6675 in Independence, Missouri. Former President Truman was issued the very first Medicare card during the ceremony. In 1965, the budget for Medicare was around $10 billion.
- In 1966, Medicares coverage took effect, as Americans age 65 and older were enrolled in Part A and millions of other seniors signed up for Part B. Nineteen million individuals signed up for Medicare during its first year.
The 70s
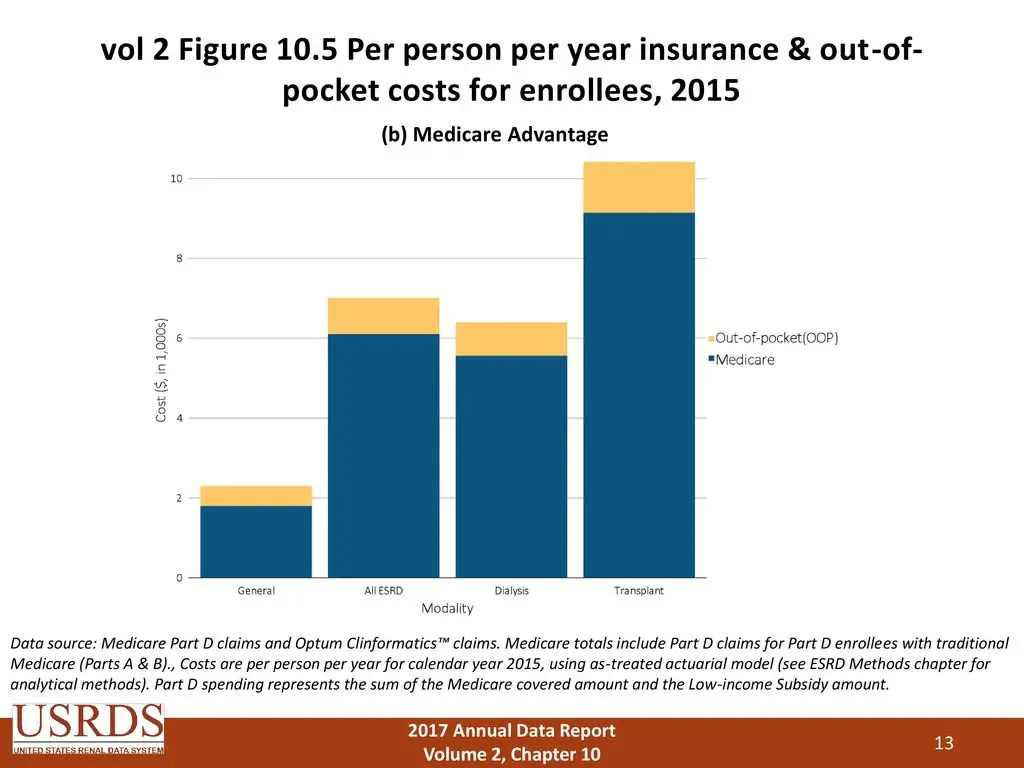
- In 1972, President Richard M. Nixon signed into the law the first major change to Medicare. The legislation expanded coverage to include individuals under the age of 65 with long-term disabilities and individuals with end-stage renal disease . People with disabilities have to wait for Medicare coverage, but Americans with ESRD can get coverage as early as three months after they begin regular hospital dialysis treatments or immediately if they go through a home-dialysis training program and begin doing in-home dialysis. This has served as a lifeline for Americans with kidney failure a devastating and extremely expensive disease.
The 80s
The 90s
The 00s
2010
- The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010 includes a long list of reform provisions intended to contain Medicare costs while increasing revenue, improving and streamlining its delivery systems, and even increasing services to the program.
2015 through 2021
Medical Infrastructure And National Health Insurance
At the same time that Medicare was passed in 1965, the Johnson administration also was interested in a program designed to counter the risks of heart disease, cancer, and stroke. The administration proposed to spend $1.2 billion over 6 years to establish 32 university-based medical complexes that would contain diagnostic and treatment centers for these diseases. The administration also favored aid to medical schoolsâinstitutional support with the objective of increasing the number of doctors and dentists available for private practice as well as $15 million for the construction and renovation of medical libraries . Variations of each of these proposals became law during the same session that Congress passed Medicare.
You May Like: When Is Open Enrollment For Medicare Supplement Plans
Medicare Part B Premiums
Medicare Part B premiums for 2021 increased by $3.90 from the premium for 2020. The 2021 premium rate starts at $148.50 per month and increases based on your income, up to to $504.90 for the 2021 tax year. Your premium depends on your modified adjusted gross income from your tax return two years before the current year.
The signup period for Medicare Parts A and B takes place at the same time as when you apply for Social Security.
The rate of $148.50 is for single or married individuals who file separate tax returns with MAGIs of $88,000 or less, and for married taxpayers who file jointly with MAGIs of $176,000 or less.
Omnibus Consolidated And Emergency Supplemental Appropriation Act
The last act to be passed in the nineties was the Omnibus Consolidated and Emergency Supplemental Appropriation Act of 1999. The most important part of this act called on the providers that paid for these specific plans. With the passing of this act, they were now subject to civil penalties.
As the 2000s began, this coverage continued to change. In 2001, the government looked to protect those that experienced sudden life changes or other changes to their health insurance policy status.
Also Check: What Age Do You Draw Medicare
When And How To Apply For Medicare
If you already receive benefits from Social Security , you will automatically be enrolled in Part B, and Part A, starting the first day of the month in which you turn 65. If you’re not receiving Social Security, though, be sure to contact the Social Security Administration about three months prior to your 65th birthday in order to receive Medicare.
There are a few other enrollment situations to be aware of, including if you’re a disabled widow or widower between age 50 and 65 but have yet to apply for disability benefits if you’re a government employee and became disabled before age 65 if you, a spouse, or dependent child has permanent kidney failure or if you’ve had Medicare Part B in the past.
Looking To The Future
Medicare faces a number of critical issues and challenges, perhaps none greater than providing affordable, quality care to an aging population while keeping the program financially secure for future generations. While Medicare spending is on a slower upward trajectory now than in past decades, total and per capita annual growth rates appear to be edging away from their historically low levels of the past few years. Medicare prescription drug spending is also a growing concern, with the Medicare Trustees projecting a comparatively higher per capita growth rate for Part D in the coming years than in the programâs earlier years due to higher costs associated with expensive specialty drugs.
To address the health care financing challenges posed by the aging of the population, a number of changes to Medicare have been proposed, including restructuring Medicare benefits and cost sharing raising the Medicare eligibility age shifting Medicare from a defined benefit structure to a âpremium supportâ system and allowing people under age 65 to buy in to Medicare. As policymakers consider possible changes to Medicare, it will be important to evaluate the potential effect of these changes on total health care spending and Medicare spending, as well as on beneficiariesâ access to quality care and affordable coverage and their out-of-pocket health care costs.
Topics
You May Like: How To Find Out If I Have Medicare
The Introduction Of Medigap Plan Standardization In 1990
There are currently 10 different Medigap plans available: A, B, C, D, F, G, K, L, M, and N. In 1980, coverage under each of these plans became standardized.
This means that no matter where you live or what company you purchase a plan from, youll be guaranteed the same basic coverage from each plan.
For example, Medigap Plan A in Boston offers the same basic coverage as Medigap Plan A in Seattle.
Solutions For The Funding Deficit
Another area in which Medicare may adapt in the future involves developing solutions for the projected funding shortfall. Due to the rising number of older adults in the U.S., the agency is facing monetary challenges. The trust fund that pays for Part A will run out of money in 2026, according to a report by the Congressional Research Service.
Congress may eventually have to decide whether and how to provide another source of funding for Part A. Measures could include raising the Medicare eligibility age or increasing premiums for people with higher incomes.
Read Also: Should I Enroll In Medicare If I Have Employer Insurance
General Fund Revenue As A Share Of Total Medicare Spending
This measure, established under the Medicare Modernization Act , examines Medicare spending in the context of the federal budget. Each year, MMA requires the Medicare trustees to make a determination about whether general fund revenue is projected to exceed 45 percent of total program spending within a seven-year period. If the Medicare trustees make this determination in two consecutive years, a “funding warning” is issued. In response, the president must submit cost-saving legislation to Congress, which must consider this legislation on an expedited basis. This threshold was reached and a warning issued every year between 2006 and 2013 but it has not been reached since that time and is not expected to be reached in the 20162022 “window”. This is a reflection of the reduced spending growth mandated by the ACA according to the Trustees.
How Much Does Medicare Cost

Original Medicare
Original Medicare is divided into Part A and Part B .
- Part A helps pay for inpatient hospital care, some skilled nursing care, home health care and hospice care.
- Part B helps pay for doctor services, outpatient hospital care, durable medical equipment, home health care not covered by Part A, and other services.Medicare was never intended to pay 100% of medical bills. Its purpose is to help pay a portion of medical expenses. Medicare beneficiaries also pay a portion of their medical expenses, which includes deductibles, copayments, and services not covered by Medicare.The amounts of deductibles and copayments change at the beginning of each year.
Part A – Monthly Premium
If you are eligible, Part A is free because you or your spouse paid Medicare taxes while you were working. You earn Social Security “credits” as you work and pay taxes. For each year that you work, you earn 4 credits.
| $458 | $471 |
You are 65 or older, and you receive or are eligible to receive full benefits fr om Social Security or the Railroad Retirement Board
You are under 65, and you have received Social Security disability benefits for 24 months You are under 65, and you have received Railroad Retirement disability benefits and you meet Social Security disability requirements You or your spouse had Medicare-covered government employment You are under 65 and have End-Stage Renal Disease
You May Like: Can You Get Medicare At Age 60
Your First Chance To Sign Up
Generally, when you turn 65. This is called your Initial Enrollment Period. It lasts for 7 months, starting 3 months before you turn 65, and ending 3 months after the month you turn 65.
Avoid the penaltyIf you miss your 7-month Initial Enrollment Period, you may have to wait to sign up and pay a monthly late enrollment penalty for as long as you have Part B coverage. The penalty goes up the longer you wait. You may also have to pay a penalty if you have to pay a Part A premium, also called Premium-Part A.
Why Did Medicare Start
The governments response to the financial ruination occurring throughout the countrys older adult population, Medicare was established to provide coverage for both in-hospital and outpatient medical services. Medicare extended health coverage to adults aged 65 and older, which meant Americans would now be financially protected when seeking medical care.
Don’t Miss: Does Medicare Cover Cgm For Type 2 Diabetes
How Did Medicare Begin
The idea of a national healthcare program originated more than 100 years ago as far back as former President Teddy Roosevelts 1912 campaign.
A serious push for a program took hold in 1945 under former President Harry Truman. He called for a national healthcare plan during his term and presented the idea to Congress. However, his proposals didnt make it through Congress at that time.
At the time, most Americans had no access to insurance after retiring. This left millions of people without coverage. In 1962, President Kennedy introduced a plan to create a healthcare program for older adults using their Social Security contributions, but it wasnt approved by Congress.
In 1964, former President Lyndon Johnson called on Congress to create the program that is now Medicare. The program was signed into law in 1965.
In recognition of his dedication to a national healthcare plan during his own term, former President Truman and his wife, Bess, were the first people to receive Medicare cards after it was signed it into law.
When first introduced, Medicare had only two parts: Medicare Part A and Medicare Part B. Thats why youll often see those two parts referred to as original Medicare today.
Parts A and B looked pretty similar to original Medicare as you may know it, although the costs have changed over time. Just like today, Medicare Part A was hospital insurance and Medicare Part B was medical insurance.
Some of major changes are discussed below.
When Did Medicare Start And Why
- Learn about the history of Medicare, the federally protected health insurance program, and the severe societal and financial problems that inspired its creation.
Ensuring access to inpatient and outpatient medical care, a wide range of specialists and diagnostic services, Medicare currently insures more than 61 million Americans or more than 18% of the population. Medicares coverage continues to expand to give beneficiaries access to the latest testing and treatment options for various conditions. But who thought of Medicare and when did Medicare start? Take a trip into history to learn about Medicares inception.
You May Like: How To Reorder Medicare Card
Medicare Part B Premiums March Higher
Of these three Medicare components, Part B is arguably the biggest wildcard when it comes to your potential out-of-pocket expenses. This argument is only enhanced by taking a look at how Medicare Part B’s monthly premium payments have evolved over the past 51 years.
Data source: Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Chart by author.
As you’ll note from the chart of Medicare Part B premiums between 1966 and 2017, the trend is higher most years. Over 51 years, the compounded annual increase in premium cost is roughly 7.7%, which is consistent with high medical care inflation rates. Medical care inflation has outpaced the inflation calculated by the Consumer Price Index for Urban Wage Earners and Clerical Workers in 33 of the past 35 years. The CPI-W is the measure used to determine whether or not Social Security recipients get a “raise” each year, and if so, by how much.
What The Medicare Advantage Commercials Say
Savage noted the ads often say: “Let us do everything! And we’re going to give you hearing and we’re going to give you dental and we’re going to pick you up and drive you to your doctor’s appointments. We’re going to give you a turkey on Thanksgiving! They promise so much.”
Omdahl told listeners: “Based on the commercials that are on television every day, people see something they think is going to be more cost effective and then they opt for that coverage without really knowing what they’re getting into.”
She’s right. A recent survey by the Kaiser Family Foundation found that seven in 10 Medicare beneficiaries didn’t compare coverage options during the most recent Open Enrollment period. And in a MedicareAdvantage.com survey of over 1,000 beneficiaries, three out of four called Medicare “confusing and difficult to understand.”
According to the Kaiser Family Foundation, the average Medicare beneficiary has a choice of 54 Medicare plans, there are 766 Medicare Part D prescription drug plans and a record 3,834 Medicare Advantage plans will be available in 2022 .
Here’s the bottom line from Omdahl and the “Friends Talk Money” hosts: Some of what you hear on those Medicare Advantage TV ads is true, but the fine print shows that “free” isn’t really “free.” When the commercials say “zero premium, zero deductible and zero co-pay,” that’s not the whole story.
Also Check: Where Can I Sign Up For Medicare
Health Insurance In The Fifties
These problems led to yet another iteration of the national health insurance idea during the fifties. As Social Security became more popular in that decade and Congress passed bills raising Social Security benefit levels in 1950, 1952, 1954, 1956, and 1958, reformers thought in terms of extending health insurance coverage to Social Security beneficiaries who were, with the exception of the dependents of deceased workers and other beneficiaries, elderly individuals . These individuals fared less well in the private health insurance market than did their younger counterparts. Many of them, after all, had lost their ties to employers, who had financed their health care . With relatively high morbidity rates, they represented a particularly bad risk for private companies to insure . The Federal Government could therefore insinuate itself as a provider of health insurance through the creation of what ultimately came to be called Medicare. First proposed publicly in 1952, this idea of limiting federally financed national health insurance to the elderly received attention in Congress beginning in 1957 .
