Medicare Vs Medicaid For Seniors
Both Medicare and Medicaid offer basic and extended health services for enrollees. Their core populations of beneficiaries are different, but seniors with low or fixed incomes may qualify for both insurance plans.
Because the enrollment, coverage and benefit details vary from person to person, and each state has its own rules about participation in Medicaid, it is always best to speak with a qualified Medicare or Medicaid counselor before making decisions about long-term health coverage.
Most plans also have case workers who can answer questions about Medicare vs Medicaid, coverage types and how to get your benefits working together.
Medicare And Medicaid Funding
Medicare is funded:
- In part by the Medicare payroll tax
- In part by Medicare recipients premiums
- In part by general federal taxes
The Medicare payroll taxes and premiums go into the Medicare Trust Fund. Bills for healthcare services to Medicare recipients are paid from that fund.
Medicaid is:
- Partially funded by the federal government
- Partially funded by each state
The federal government pays an average of about 60% of total Medicaid costs, but the percentage per state ranges from 50% to about 78%, depending on the average income of the state’s residents .
Under the ACA’s expansion of Medicaid, however, the federal government pays a much larger share.
For people who are newly eligible for Medicaid due to the ACA , the federal government pays 90% of the cost, while the states pay just 10% of the cost.
Medicaid Vs Private Insurance
At their most basic, Medicaid and private insurance offer health coverage, but their inner workings are different. Medicaid is a state and federally funded program that covers the cost of medical services for low-income parents, children, pregnant women, older adults, those living with disabilities, and women with cervical or breast cancer. These individuals must meet the qualifying income requirements and satisfy other eligibility requirements.
Whether your income level qualifies you or your family for Medicaid depends on your household size and the program youre applying for.
Although the federal government sets the minimum standards for Medicaid, this program gives states a lot of flexibility to customize their programs, including whom to cover, the benefits to provide, and how health care services are delivered. While there are mandatory benefits states must cover, theres also room to cover additional optional benefits.
Payment rates for Medicaid providers and program administrative costs are low, which makes Medicaid a lower-cost coverage compared with private insurance. The result is that beneficiaries can enjoy more-comprehensive benefits at decreased out-of-pocket costs with Medicaid than with private health insurance. In fact, its cheaper to cover adults of similar health status through Medicaid than private insurance.
Don’t Miss: How To Sign Up For Medicare At Age 65
Medicaid Covers A Broad Range Of Health And Long
Medicaid covers a broad range of services to address the diverse needs of the populations it serves . In addition to covering the services required by federal Medicaid law, many states elect to cover optional services such as prescription drugs, physical therapy, eyeglasses, and dental care. Coverage for Medicaid expansion adults contains the ACAs ten essential health benefits which include preventive services and expanded mental health and substance use treatment services. Medicaid plays an important role in addressing the opioid epidemic and more broadly in connecting Medicaid beneficiaries to behavioral health services. Medicaid provides comprehensive benefits for children, known as Early Periodic Screening Diagnosis and Treatment services. EPSDT is especially important for children with disabilities because private insurance is often inadequate to meet their needs. Unlike commercial health insurance and Medicare, Medicaid also covers long-term care including both nursing home care and many home and community-based long-term services and supports. More than half of all Medicaid spending for long-term care is now for services provided in the home or community that enable seniors and people with disabilities to live independently rather than in institutions.
Figure 5: Medicaids benefits reflect the needs of the population it serves.
Medicaid Covers 1 In 5 Americans And Serves Diverse Populations
Medicaid provides health and long-term care for millions of Americas poorest and most vulnerable people, acting as a high risk pool for the private insurance market. In FY 2017, Medicaid covered over 75 million low-income Americans. As of February 2019, 37 states have adopted the Medicaid expansion. Data as of FY 2017 show that 12.6 million were newly eligible in the expansion group. Children account for more than four in ten of all Medicaid enrollees, and the elderly and people with disabilities account for about one in four enrollees.
Medicaid plays an especially critical role for certain populations covering: nearly half of all births in the typical state 83% of poor children 48% of children with special health care needs and 45% of nonelderly adults with disabilities and more than six in ten nursing home residents. States can opt to provide Medicaid for children with significant disabilities in higher-income families to fill gaps in private health insurance and limit out-of-pocket financial burden. Medicaid also assists nearly 1 in 5 Medicare beneficiaries with their Medicare premiums and cost-sharing and provides many of them with benefits not covered by Medicare, especially long-term care .
Figure 4: Medicaid plays a key role for selected populations.
Don’t Miss: What Does Medicare Cover Australia
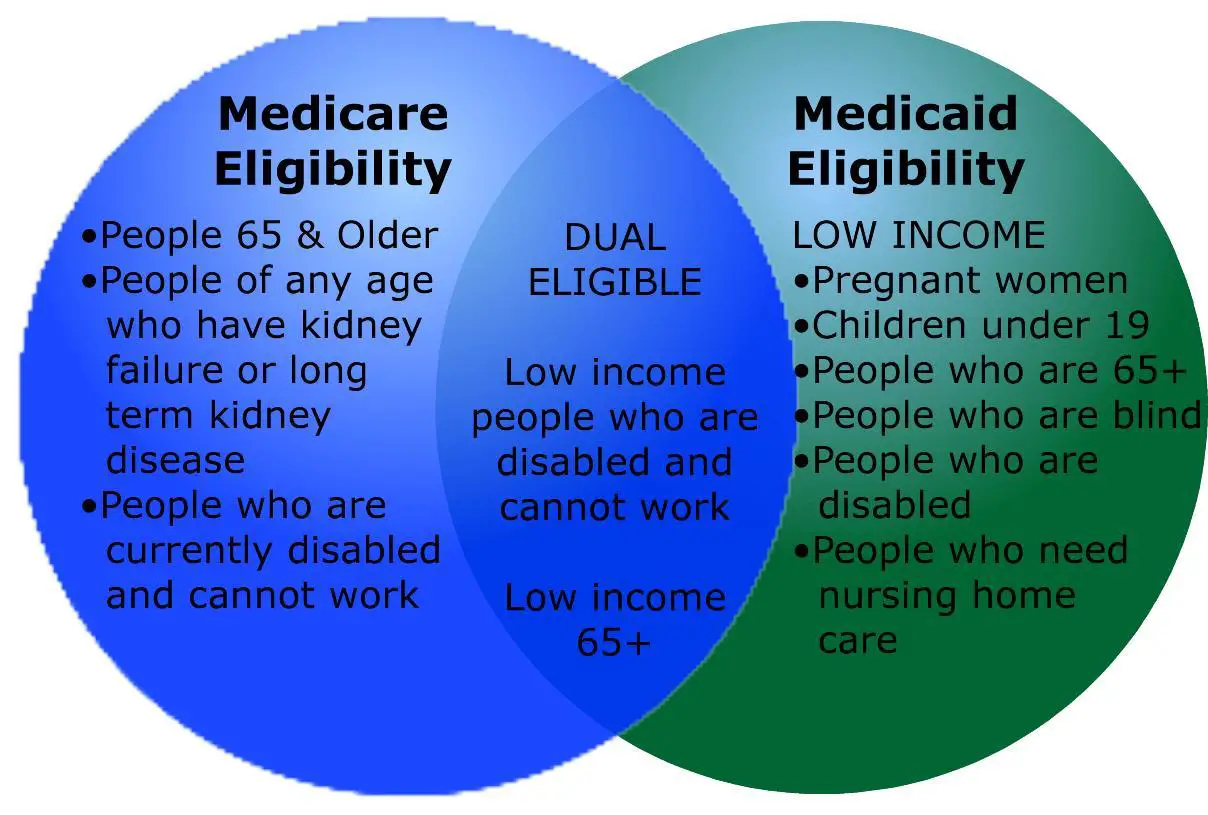
Can You Have Both
People who qualify for both Medicare and Medicaid are considered dual eligible. In this case, you may have original Medicare or a Medicare Advantage plan , and Medicare will cover your prescription drugs under Part D.
Medicaid may also cover other care and drugs that Medicare doesnt, so having both will probably cover most of your healthcare costs.
Medicare Vs Medicaid: Are They The Same Thing
Americans have two government programs to turn to when paying their health care costs: Medicare and Medicaid. Medicare is a national health insurance program designed to help people 65 and older and those with disabilities pay their medical bills. Medicaid is a collection of state-run programs that gives low-income Americans access to affordable care.
While their names sound similar, and they both help people pay for health care, Medicare and Medicaid have different eligibility requirements, coverages, and costs. Understanding which you need and how you might qualify for these government-funded programs could affect how much you spend on health care. Heres a look at how the Medicare and Medicaid programs differand how you could possibly receive benefits from each.
Read Also: How To Pay For Medicare Without Social Security
Policy Basics: Introduction To Medicaid
In 2018, Medicaid provided health coverage for 97 million low-income Americans.
In 2018, Medicaid provided health coverage for 97 million low-income Americans over the course of the year. In any given month, Medicaid served 32 million children, 28 million adults , 6 million seniors, and 9 million people with disabilities, according to Congressional Budget Office estimates.
Children account for more than two-fifths of Medicaid enrollees but only one-fifth of Medicaid spending. Only one-fifth of Medicaid enrollees are seniors or people with disabilities, but because they need more health care services, they account for nearly half of Medicaid spending.
Medicaid is sometimes confused with Medicare, the federally administered, federally funded health insurance program for people over 65 and some people with disabilities. And there is overlap between the two programs: nearly 10 million low-income seniors and people with disabilities so-called dual eligibles are enrolled in both Medicare and Medicaid.
What Services Does Medicaid Cover
Medicaid covers more than 60 percent of all nursing home residents and roughly 50 percent of costs for long-term care services and supports.
Federal rules require state Medicaid programs to cover certain mandatory services, such as hospital and physician care, laboratory and X-ray services, home health services, and nursing facility services for adults. States are also required to provide a more comprehensive set of services, known as the Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnostic, and Treatment benefit, for children under age 21.
States can and all do cover certain additional services as well. All states cover prescription drugs, and most cover other common optional benefits include dental care, vision services, hearing aids, and personal care services for frail seniors and people with disabilities. These services, though considered optional because states are not required to provide them, are critical to meeting the health needs of Medicaid beneficiaries.
About three-quarters of all Medicaid spending on services pays for acute-care services such as hospital care, physician services, and prescription drugs the rest pays for nursing home and other long-term care services and supports. Medicaid covers more than 60 percent of all nursing home residents and roughly 50 percent of costs for long-term care services and supports.
How Much Does Medicaid Cost? How Is It Financed?
Read Also: Why Is My First Medicare Bill For 5 Months
What Is Medicare What Is Medicaid
Medicare is a federal program generally for people who are 65 or older or have a qualifying disability or medical condition. Medicare Part A and Part B are provided by the federal government, and Medicare Part C and Part D, while federally governed, are provided by private insurance companies.
Medicaid is a state government program that helps pay health care costs for people with limited income and resources, and different programs exist for specific populations. Medicaid plans vary from state-to-state but follow federal guidelines for benefits.
Medicaid Facilitates Access To Care
A large body of research shows that Medicaid beneficiaries have far better access to care than the uninsured and are less likely to postpone or go without needed care due to cost. Moreover, rates of access to care and satisfaction with care among Medicaid enrollees are comparable to rates for people with private insurance . Medicaid coverage of low-income pregnant women and children has contributed to dramatic in the U.S. A growing body of research indicates that Medicaid eligibility during childhood is associated with reduced teen mortality, improved long-run educational attainment, reduced disability, and lower rates of hospitalization and emergency department visits in later life. Benefits also include second-order fiscal effects such as increased tax collections due to higher earnings in adulthood. Research findings show that state Medicaid expansions to adults are associated with increased access to care, improved self-reported health, and reduced mortality among adults.
Figure 7: Nationally, Medicaid is comparable to private insurance for access to care the uninsured fare far less well.
Read Also: Does Medicare Advantage Cover Chiropractic Care
Medicare Vs Medicaid: Whats The Difference
Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This may influence which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list ofour partnersandhere’s how we make money.
Medicare and Medicaid are government-run health care programs meant to serve different populations:
-
Medicare is an insurance program that primarily serves people 65 and older, regardless of income.
-
Medicaid is an assistance program that provides health insurance to low-income people of all ages.
Some people get both Medicare and Medicaid. Medicaid can help pay Medicare premiums, deductibles and copays for impoverished people. Medicaid also can pay for nursing home and personal care services, expenses that arent typically covered by Medicare.
What Is The Difference Between Medicare And Medicaid Programs
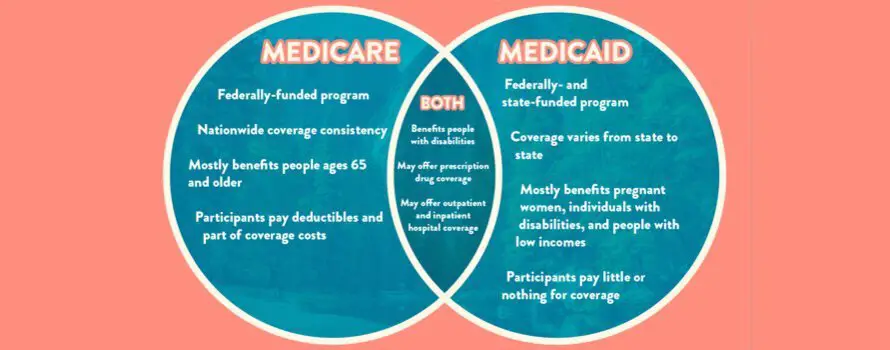
The difference between Medicare and Medicaid programs is that Original Medicare is administered strictly by the federal government, while Medicaid is managed by both federal and state officials. The Medicaid and Medicare programs also differ in that your income doesnt matter for Medicare eligibility, whereas Medicaid coverage tends to be for those with a lower income level.
You May Like: Does Medicare Medicaid Cover Assisted Living
How Do I Get Medicare And Medicaid
Looking to determine your eligibility for Medicaid, Medicare, or both? HealthMarkets can show you what kinds of coverage you may qualify for by asking just a few questions. If youre eligible for both Medicaid and Medicare, a licensed insurance agent can help you find the right Dual Eligible Special Needs Medicare Advantage plan for your needs. If you dont qualify for both, you can still get a free quote for a Medicare Supplement plan, or shop, compare, and enroll in a Medicare Advantage plan today. Get started!
48241-HM-1221
Medicare Gives Many Options
Medicare offers a wealth of choices. Once you decide whether you want a Medicare Advantage or Original Medicare plus Part D, youre able to narrow your focus and select the best Medicare plan for you.
Premiums, deductibles and out-of-pocket costs can vary greatly, so make sure you compare each cost.
Medicaid, on the other hand, will likely give you one or very few choices. That plan could be through the state, or it could be a managed care plan offered by a private insurer.
Differences arent just between Medicare and Medicaid. The different types of Medicare plans also vary. Heres how Medicare and Medicaid plans compare:
Don’t Miss: What Are All The Parts Of Medicare
Compare Health Insurance Plans For Retirees
If youre looking for health insurance coverage as a retiree, its good to take advantage of any government programs you qualify for and shop around to ensure that you have the coverage you need. For example, even if you qualify for Medicare, you may need to purchase supplemental plans for services that are not covered, like dental work.
When evaluating different plans, there are a few different factors that you should consider. You should make sure that the insurance company has in-network providers in your area and they offer a plan that meets your specific health needs. You should also compare policy premiums and deductibles, waiting periods, and customer satisfaction.
Covering Your Retirement Expenses
- From healthcare expenses to dream vacations, retirement is full of expenses that youll need to cover without the benefit of a regular paycheck. Put together a prospective retirement budget and then use our retirement calculator to see if your savings are enough to cover those expenses.
- Between saving rates, investing plans and tax issues, there are a lot of factors that go into a sound retirement plan. Thats why many people choose to work with financial advisors, many of whom specialize in retirement planning strategies. SmartAssets financial advisor matching tool can help you find a local advisor today. Just answer some questions about your financial state and goals, and the tool will match you with up to three advisors in your area.
You May Like: What Is Medicare Chronic Care Management
Services That Medicare Does Not Provide
If Medicare does not cover a medical expense or service, a person may wish to take out a Medigap plan for supplemental coverage.
Private companies also offer Medigap plans. Depending on the individual plan, Medigap may cover:
- copayments
- deductibles
- care outside of the U.S.
If a person has a Medigap policy, Medicare will first pay their eligible portion. Afterward, Medigap will pay the rest.
To have a Medigap policy, a person must have both Medicare Parts A and B and pay a monthly premium.
Medigap policies do not cover prescription drugs, which a Part D plan covers.
An individual must be one of the following to be eligible for Medicare:
- age over 65 years
- age under 65 years and living with a disability
- any age with end stage renal disease or permanent kidney failure needing dialysis or transplant
They must also be:
- a U.S. citizen or permanent legal resident for 5 years continuously
- eligible for Social Security benefits with at least 10 years of contributing payment
Basis Of Eligibility And Maintenance Assistance Status
Medicaid does not provide medical assistance for all poor persons. Under the broadest provisions of the Federal statute, Medicaid does not provide health care services even for very poor persons unless they are in one of the following designated groups. Low income is only one test for Medicaid eligibility for those within these groups their resources also are tested against threshold levels .
States generally have broad discretion in determining which groups their Medicaid programs will cover and the financial criteria for Medicaid eligibility. To be eligible for Federal funds, however, States are required to provide Medicaid coverage for certain individuals who receive federally assisted income-maintenance payments, as well as for related groups not receiving cash payments. In addition to their Medicaid programs, most States have additional State-only programs to provide medical assistance for specified poor persons who do not qualify for Medicaid. Federal funds are not provided for State-only programs. The following enumerates the mandatory Medicaid categorically needy eligibility groups for which Federal matching funds are provided:
Also Check: What Is A Medicare Wellness Checkup
How Medicaid Works With Other Coverage
You may still qualify for Medicaid even if you have other health insurance coverage, and coordination of benefits rules decide who pays your bill first. In this case, your private insurance, whether through Medicare or employer-sponsored, will be the primary payer and pays your health care provider first. Medicaid comes in as second insurance to settle what your private insurance doesnt pay, up to its limit.
If you have both Medicaid and private health insurance, you should show both your private health insurance card and Medicaid card to your medical provider every time you receive services.
A health-service provider who accepts both your Medicaid and private insurance card wont bill you for copayments or deductibles.
Any money received from an insurance company or as compensation for a medical care lawsuit must be used to pay the health provider. If Medicaid already has covered the cost of care, you must make a refund to Medicaid. If your private insurance is through an employer-sponsored plan, you may be an eligible candidate for the Health Insurance Premium Payment program. HIPP is a voluntary program that may pay your insurance premium as long as you or a family member qualifies for Medicaid coverage.
If your service provider wont take your Medicaid and private insurance card, your insurance company may help you locate a doctor in its provider network.
