What Are The Differences Between Medicare And Medicaid
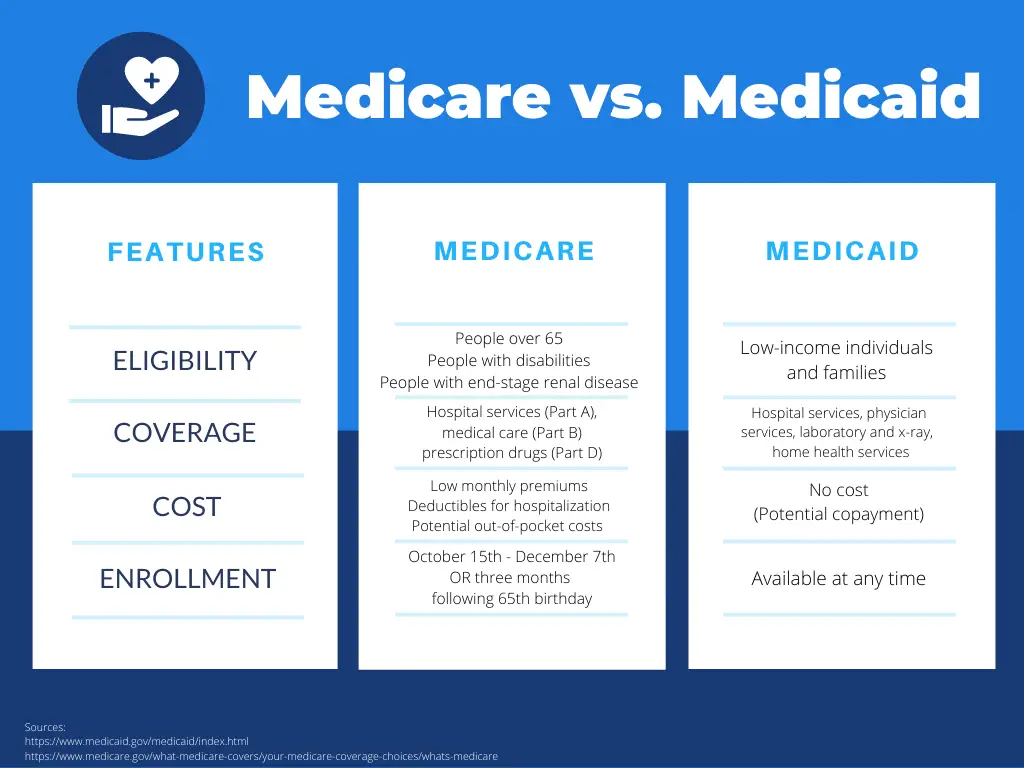
Medicare is a federal health insurance program open to Americans aged 65 and older, and those with specific disabilities who are under the age of 65. Medicaid, a combined state and federal program, is a state-specific health insurance program for low-income individuals with limited financial means, regardless of their age.
Medicare, generally speaking, offers the same benefits to all eligible participants. However, coverage is divided into Medicare Part A, Part B, and Part D. Medicare Part A is for hospice care, skilled nursing facility care, and inpatient hospital care. Medicare Part B is for outpatient care, durable medical equipment, and home health care. Part D is for prescription coverage. Not all persons will elect to have coverage in all three areas. In addition, some persons choose to get their Medicare benefits via Medicare Advantage plans, also called Medicare Part C. These plans are available via private insurance companies and include the same benefits as Medicare Part A and Part B, as well as some additional ones, such as dental, vision, and hearing. Many Medicare Advantage plans also include Medicare Part D.
Medicaid is more comprehensive in its coverage, but the benefits are specific to the age group. Children have different eligibility requirements and receive different benefits from low-income adults and from elderly or disabled persons.
Helpful Resources
Who Does Medicare Cover
Medicare is a federal government-sponsored healthcare program for those 65 and over, and for younger people who are disabled. Most people with Medicare paid FICA taxes during their working years, and realize the benefits of that tax through Medicare coverage. The federal government establishes the eligibility criteria for Medicare.
What Do Medicare Part A And Part B Have In Common
Medicare Part A and Part B share some characteristics, such as:
- Both are parts of the government-run Original Medicare program.
- Both may cover different hospital services and items.
- Both may cover mental health care .
- Both may cover home health care.
- Both have annual deductibles, as well as coinsurance or copayments, that may apply to certain services.
- Both have monthly premiums, although many people dont have to pay the Part A premium .
You May Like: Are Chemotherapy Drugs Covered By Medicare
Medicare Vs Medicaid For Seniors
Both Medicare and Medicaid offer basic and extended health services for enrollees. Their core populations of beneficiaries are different, but seniors with low or fixed incomes may qualify for both insurance plans.
Because the enrollment, coverage and benefit details vary from person to person, and each state has its own rules about participation in Medicaid, it is always best to speak with a qualified Medicare or Medicaid counselor before making decisions about long-term health coverage.
Most plans also have case workers who can answer questions about Medicare vs Medicaid, coverage types and how to get your benefits working together.
Opting For Part A Only
Some people choose only to have Medicare Part A coverage so that they dont have to pay the monthly premiums for Medicare Parts B and D. If you still have insurance through a current employer , you can add the other parts later with no penalty.
However, if you decline Parts B and D and don’t have another insurance plan in place, you’ll face a late enrollment penalty when you add the other parts later.
In the past, Medicaid programs typically didn’t offer a lot of choice in terms of plan design. Today, most states utilize Medicaid managed care organizations . If there’s more than one MCO option in your area of the state, you will likely be given the option to select the one you prefer.
Recommended Reading: Does Medicare Pay For Stem Cell Knee Replacement
Medicare And Medicaid: What Is The Difference
The federal and state partnership has established different Medicaid plans for each state. Through the Affordable Care Act , which was signed into law in 2010, President Barack Obama tried to expand health care coverage to more Americans. Therefore, all legal residents and citizens of the United States with an income below 138% of the poverty line are eligible for Medicaid participating state insurance.
Although ACA has been working to expand federal funding and eligibility for Medicaid, the US Supreme Court ruled that states can continue to receive the established level of Medicaid funding without participating in the expansion. Therefore, many states choose not to expand funding levels and eligibility requirements.
People covered by Medicaid dont have to pay anything for covered services. Unlike Medicare, which is available to almost every American 65 and older, Medicaid has strict eligibility requirements that vary from state to state.
However, because the program is designed to help the poor, many states have strict requirements, including income restrictions. For a breakdown of eligibility requirements by state, please visit Medicaid.gov and BenefitsCheckUp.org.
How Does Medicare Work
Medicare is funded partially by payroll taxes and partially by general government revenue and state government payments. Medicare recipients must also pay monthly premiums for their coverage and will need to pay co-pays for some services. However, these premiums and co-pays are usually much lower than private health insurance options.
The Original Medicare program contains Part A and Part B coverage. Part A covers inpatient hospital stays, and beneficiaries do not need to pay a monthly premium. Part B covers a range of outpatient medical services and preventative doctors visits, and beneficiaries will need to pay a low monthly premium. However, these premiums are can be deducted from your Social Security benefits if you are already receiving them.
Those who qualify for Medicare can choose to purchase supplementary coverage as well. There are three different types of supplementary coverage Medicare Advantage, Medigap, and Part D, all of which require you to pay an additional monthly premium. Medicare Advantage, which is sometimes referred to as Part C, is a group of supplementary plans offered by private insurers. These plans replace your Original Medicare and provide additional benefits.
Alternatively, you can choose to purchase a Medigap plan, which is used in addition to Parts A and B to provide additional coverage. Part D plans provide coverage for prescription drugs, which are not covered in Original Medicare.
You May Like: Does Humana Offer A Medicare Supplement Plan
Medicare Vs Medicaid Benefits
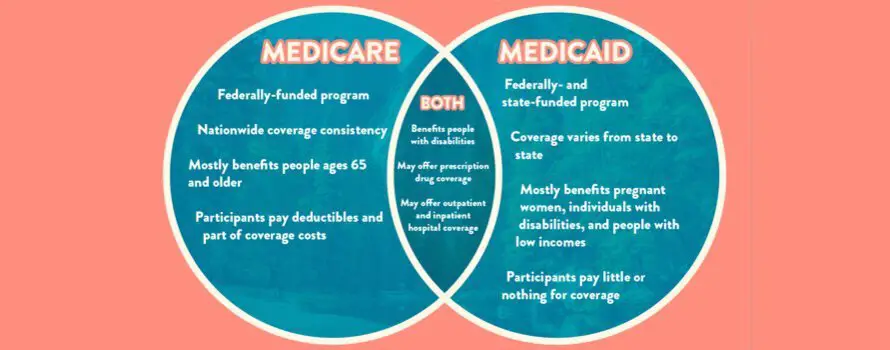
Medicare and Medicaid are different programs that offer some overlapping benefits. Where they differ is mainly in their eligibility standards and their methods of delivering care.
Medicare is principally intended for seniors aged 65 and over, while Medicaid is mainly intended for low-income citizens and members of at-risk groups.
Medicare Vs Medicaid: Differences In Covered Services
Medicaid benefits differ by state, but every state must cover certain kinds of care. These include nursing home and home health care, lab-work and x-ray diagnostic services, inpatient and outpatient hospital services, transportation to a medical facility, and tobacco recess counseling for pregnant women.
Besides paying Medicare-related costs like doctors, hospitalization, and medicines, Medicaid offers two other types of care that Medicare doesnt:
- Custodial care or personal care: This helps you with day-to-day activities.
- Nursing home care: Medicaid is the main provider of long-term nursing home care. Medicare will cover skilled nursing short-term, but it doesnt cover prolonged care.
Because Medicare has very restricted coverage for nursing homes, seniors in need of it may try to qualify for Medicaid.
You May Like: Does Medicare Pay For In Home Hospice Care
The Difference Between Medicare And Medicaid
Created by FindLaw’s team of legal writers and editors
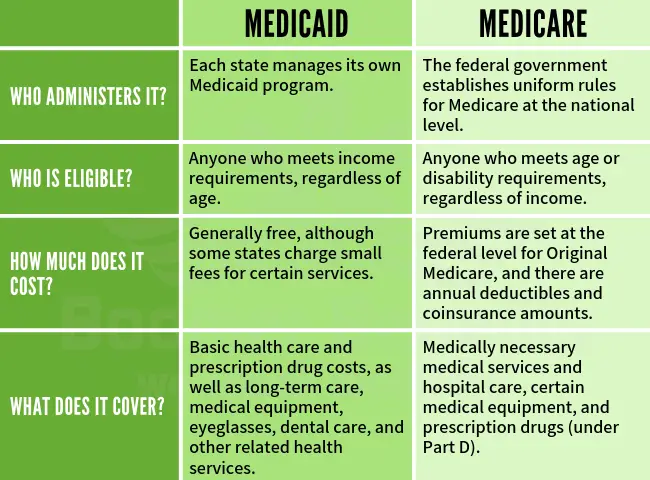
Medicare and Medicaid are both federal healthcare programs intended to help those in need and/or who’ve reached a certain age, but there are some key distinctions. The differences between Medicare and Medicaid generally can be boiled down to who runs them, who qualifies for them, how much users pay, and what services they cover. The following article will help you get a handle on the key differences between the two.
Can You Get Insurance To Help Cover Part A And Part B Expenses
As youve seen in this article, Medicare Part A and Part B generally come with out-of-pocket costs for you to pay. Did you know that you might be able to buy a Medicare Supplement insurance plan to help cover those expenses? There are up to 10 standardized Medicare Supplement plans available in most states. Learn more about Medicare Supplement insurance.
You can compare Medicare Supplement plans and Medicare coverage options anytime you like, with no obligation. Type your zip code in the box on this page to begin.
The product and service descriptions, if any, provided on these Medicare.com Web pages are not intended to constitute offers to sell or solicitations in connection with any product or service. All products are not available in all areas and are subject to applicable laws, rules, and regulations.
New To Medicare?
Becoming eligible for Medicare can be daunting. But don’t worry, we’re here to help you understand Medicare in 15 minutes or less.
Recommended Reading: Who Can Get Medicare Part D
Four Main Parts To Medicare
⢠Part A: Hospital/Hospice Insurance
⢠Part B: General medical insurance . Must elect at 65 or be penalized for the lifetime unless the senior citizen is otherwise fully insured.
⢠Part C: Medicare Advantage . This is an HMO. Medicare Part C is elected instead of Part A & B and typically provides more services, including prescriptions. Usually covers the 20% not covered subject to co-pays/deductibles.
⢠Part D: Prescription Drugs . Enrollee pays deductible , then 25% up to a certain amount. Then pays a higher percentage of another threshold up to yet a third threshold when the patient pays only 5%. The coverage between 2nd and 3rd threshold is called the “donut hole.”
Medicare Supplements: If getting Part A and B , the supplement will cover other 20% .This will also referred to as Medigap.
What Is The Difference Between Medicare And Medicaid In America
The Medicare program primarily covers older adults, while Medicaid covers low-income people and families. Medicare and Medicaid are two government-sponsored health insurance programs available to Americans. Medicare covers most people 65 and older, while Medicaid provides health insurance to low-income individuals and families.
You May Like: Does Medicare Require A Referral For A Colonoscopy
Original Medicare: Part A And Part B
Medicare Part A and Part B make up the federal program known as Original Medicare. Learn more about how you qualify for Medicare.
- If youre eligible for Medicare Part A and Part B, you might be enrolled automatically.
- If youre getting Social Security benefits when you turn 65, youre typically enrolled without having to do anything.
- If youre under 65 and get disability benefits, you may be enrolled in Medicare Part A and Part B automatically. Read the details of when youll get enrolled in Part A and Part B if you qualify for Medicare due to disability.
Be aware, though, that sometimes youre not automatically enrolled, and you have to take steps to enroll in Medicare. For example:
- If you have end-stage renal disease , you might qualify for Medicare before youre 65, but you have to sign up through Social Security.
- If you live in Puerto Rico, even if youre automatically enrolled in Medicare Part A, you need to enroll manually in Medicare Part B.
- If you delayed enrollment in Medicare Part A and/or Part B beyond your Medicare Initial Enrollment Period, you need to enroll manually.
This might not be a complete list of occasions when you have to enroll manually.
Contact Your Local State Health Insurance Assistance Program
Based on the information you provided, you do not appear to be eligible for Medicare cost-saving programs.
Each state offers a State Health Insurance Assistance Program , partly funded by the federal government, to give you free counseling and assistance. A SHIP counselor may be available by phone or in person.
Visit www.shiptacenter.org to find your local SHIP office.
Don’t Miss: How Much Does Medicare Pay For Hospice
Medicare Disability Vs Medicaid Disability:
If youre disabled, the question of whether Medicare disability or Medicaid disability is right for you may feel even more complicated because there are a few more steps and rules to consider.
Essentially, if youre disabled and are approved for Social Security disability insurance benefits, you will be eligible to receive Medicare, but not until after youve received 24 months of payments. So while your SSDI eventually gives you access to receiving Medicare benefits, it may be two years before thats a legitimate option for you.
However, if youre approved for Supplemental Security Income youll be immediately eligible to receive Medicaid. There is no waiting period for SSI recipients to receive Medicaid. In most states, once youre determined to be eligible for SSI, youll automatically be enrolled in Medicaid.
What Is Medicare Part A
Medicare Part A is hospital insurance. It may cover your care in certain situations, such as:
- Youre admitted to a hospital or mental hospital as an inpatient.
- Youre admitted to a skilled nursing facility and meet certain conditions.
- You qualify for hospice care.
- Your doctor orders home health care for you and you meet the Medicare criteria. Medicare Part A may cover part-time home health care for a limited time.
Even when Medicare Part A covers your care:
- You may have to pay a deductible amount and/or coinsurance or copayment.
- There may be some services you get in a hospital or other setting that Medicare doesnt cover.
- Its possible that your Part A coverage will run out for example, if you stay in the hospital for more than 90 days in a row, you might have to pay all costs. Learn more about Medicare Part A
- Medicare typically wont pay for a private room or non-medical items such as toiletries or a television in your room.
Don’t Miss: Is Medical Part Of Medicare
Can You Have Both Medicare And Medicaid
In some cases, you can be eligible for both Medicaid and Medicare its referred to as dual eligible. With both Medicare and Medicaid coverage, the programs will cover practically all of your health expenses.
For dual eligibles, Medicare is the primary coverage and pays first. Medicaid pays second for anything that isnt covered. Medicare can cover your Part D prescription drugs while Medicaid may cover some drugs and other care not covered by Medicare.
Some states have a Medicare-Medicaid Plan which coordinates your Medicare and Medicaid benefits. Depending on your eligibility, you may qualify for a Dual Eligible Special Needs Plan with some state-covered costs.
Just because youre eligible for one doesnt mean you qualify for the other. Medicare status is determined by age or disability while Medicaid status is determined by income, says Dodge. It is important to check both since you may qualify for better benefits and reduced out-of-pocket expenses if you do.
What Is Medicare What Is Medicaid
Medicare is a federal program generally for people who are 65 or older or have a qualifying disability or medical condition. Medicare Part A and Part B are provided by the federal government, and Medicare Part C and Part D, while federally governed, are provided by private insurance companies.
Medicaid is a state government program that helps pay health care costs for people with limited income and resources, and different programs exist for specific populations. Medicaid plans vary from state-to-state but follow federal guidelines for benefits.
You May Like: When Can I Enroll For Medicare Part B
Can You Have Medicare And Medicaid
It is possible to have both Medicare and Medicaid. This is dual-eligibility. Individuals who are dual-eligible are usually adults over 65 with a low-income, or a low-income person with a disability such as End-Stage Renal Disease or ALS.
If you are dual-eligible for Medicare and Medicaid, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services collaborate to make sure your benefits from each program work together. The CMS has an extensive collection of resources for people who are dual-eligible who have questions about coordinating their benefits.
How GoMedigap Can Help
Do you have questions regarding the differences between Medicare and Medicaid? Do you believe you might be dual-eligible and want to check on your benefits? We can help. Contact one of our friendly, knowledgeable agents, and we can help explains the similarities, differences, and the benefits you get from these health programs.
Nothing on this website should ever be used as a substitute for professional medical advice. You should always consult with your medical provider regarding diagnosis or treatment for a health condition, including decisions about the correct medication for your condition, as well as prior to undertaking any specific exercise or dietary routine.
Can One Have Dual Eligibility For Both Medicare And Medicaid
Yes, Medicare and Medicaid are not mutually exclusive programs. Persons who are eligible for both are referred to as having Dual Eligibility, Dual Eligibles, or often simply Duals. Medicare is the first payer of covered benefits, while Medicaid is the secondary payer. Typically, Medicaid will pay for Medicare premiums and co-payments for dual eligibles. In fact, many states have special programs intended to make it easier for seniors to manage their dual eligibility status as it can be confusing to know where to turn for what services. This is generally in the form of managed care.
There are also programs called Medicare Saving Programs for low-income seniors that dont quite qualify for Medicaid.
Recommended Reading: Does Medicare Require A Referral To See A Podiatrist
Eligibility For Medicare Vs Medicaid
To be eligible for Medicare you must be 65 years old or have a disability. There are other conditions that will qualify you for Medicare, however, these are the most common eligibility requirements.
Medicaid eligibility will be determined by your income. Medicaid is a health insurance plan that covers low-income families, children, pregnant women, and seniors.
